Bentonite is a lamellar structure of silicates; the main component is montmorillonite; the cations between the layers are easily exchanged, with a large ion exchange capacity. Bentonite is a non-metallic mineral with various uses, enjoying the name of “universal” clay. According to the montmorillonite layer, it can be exchanged between the types of cations; the content of bentonite is divided into sodium bentonite, calcium bentonite, magnesium bentonite, and aluminum (hydrogen) bentonite. This paper focuses on the introduction of different properties of bentonite, including performance, method, and application areas.
01, The overview of bentonite
Bentonite is a lamellar structure of silicates; the main component is montmorillonite; the cations between the layers are easily exchanged, with a large ion exchange capacity. The term “bentonite” is derived from the name of the clay-producing region in Wyoming, USA, and is also called “bentonite” or “bentonite.” Pure bentonite is rare; most contain varying amounts of impurities such as quartz, feldspar, mica, zeolite, and pyrite. Bentonite is usually white, but also light gray, cheese color, light red, flesh red, brick red, maroon, yellow-green, black, mottled color, etc., greasy luster, waxy luster or earthy luster, shell-like or jagged fracture.
Bentonite has good physical and chemical properties. It is known as “universal clay,” and it can be used as a binder, suspending agent, thixotropic agent, stabilizer, purification, and decoloration agent, filling material, feed, catalysts, etc., and is widely used in metallurgy, petroleum, foundry, food, chemical industry, environmental protection, and other industrial sectors.
Montmorillonite content is generally more than 65%, so its nature determines the nature of bentonite. Montmorillonite’s main component is silica-alumina and contains a small amount of magnesium, calcium, potassium, sodium, iron, and other ions; its chemical formula: (Na, Ca)0.33(Al, Mg, Fe)2[(Si, Al)4O10](OH)2-nH2O. Its structure comprises two silica-oxygen tetrahedra sandwiched in an aluminum-oxygen octahedral composition of the 2:1 type crystal structure.
1.1 Structural properties of bentonite
Bentonite mainly comprises dioctahedral montmorillonite bedrock, with other mineral components such as illite, kaolinite, chlorite, and eclogite. It is well known that the montmorillonite content is representative of the grade of bentonite. Literature shows that the montmorillonite unit half-crystalline cell structure general formula is:
The crystal cell structure exhibits 2:1-type layered silicate properties. The structural unit layer is composed of Si-O4 tetrahedra interspersed with an AlO4(OH)2 octahedron. The oxygen atom at the tip of each tetrahedron points to the center of the structural layer and is shared with the octahedron.
1.2 China’s bentonite resources and its chemical composition
Bentonite can be divided into calcium-based, sodium-based, lithium-based, and hydrogen-based bentonite according to its interlayer cation species. At present, more than 90% of the bentonite found in the exploration belongs to calcium-based soil, with montmorillonite content between 65 and 90%, and impurities are mainly a small amount of quartz, feldspar, mica, kaolinite, chlorite, calcite, and organic matter and so on. Its principal mineral chemical composition is silicon oxide, alumina, water, and a small amount of iron oxide, manganese dioxide, magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, titanium dioxide, etc. The origin and geology of bentonite will directly affect its mineral composition and chemical properties but also determine the physical and chemical properties and aplicación de bentonita.
02, The classification of bentonite
According to the montmorillonite interlayer exchangeable cation species, the content of bentonite is divided into sodium-based bentonite, calcium-based bentonite, magnesium-based bentonite, and aluminum (hydrogen)— —based bentonite. The interlayer domain of bentonite is the distance between its structural lamellae. Because the interlayer domain has the advantages of interlayer exchange, interlayer polymerization, interlayer column support, and interlayer adsorption are used as environmental adsorbent materials. The type and amount of interlayer cations determine the classification of bentonite. If sodium ions dominate the interlayer, the bentonite belongs to sodium-based bentonite; if calcium ions dominate the interlayer, the bentonite belongs to calcium-based bentonite. The type of bentonite determines its layer spacing; bentonite layer spacing is generally 0.96 ~ 2.14nm; calcium bentonite layer spacing is about 15nm; sodium bentonite layer spacing is about 1.2nm.
Chemical composition of sodium-based bentonite and lithium-based bentonite
In recent years, through column support, ion exchange, and other methods to adjust the layer spacing of bentonite, changing its properties to prepare functional materials has become a hot spot in various fields of research.
2.1 Sodium-based bentonite
Guo Guangsi [6] and others in the sodium bentonite on bauxite coating properties of the article, the use of bauxite and talc as a refractory aggregate, sodium bentonite and CMC as a composite suspending agent, sodium hexametaphosphate and water glass binder, water as a carrier, adding the appropriate amount of antifoaming agent and surfactant. 0.5% of the CMC, 5% water glass, sodium hexametaphosphate, and 6% (the amount of each ingredient to join). (for the mass fraction of refractory aggregate). Change the amount of sodium bentonite to test the density of the coating, pH, viscosity, suspension, leveling, the amount of coating, drip, strength, and other properties to study the effect of sodium bentonite on the performance of the coating. The test found that the sodium bentonite added 5%, the coating had the best overall performance.
2.2 Calcium bentonite
Physical and chemical properties of calcium bentonite
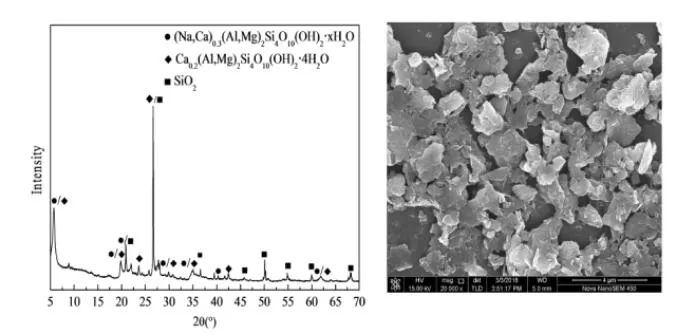
Calcium-based bentonite XRD image (left) and SEM image (right)
The left is the XRD figure of calcium-based bentonite, and the right is the SEM figure of calcium-based bentonite; from the analysis, it can be seen that calcium-based bentonite has a lamellar structure, an irregular distribution, the particle size distribution is very uneven, and there is no specific shape.
Jiang Lei [7] in the new calcium-based bentonite grounding composite material resistance reduction and anti-wear research on the commonly used metal and carbon conductive particles and common corrosion inhibitors on the market for pre-selection, and then use orthogonal experiments to determine the optimal mass fraction of each component of calcium-based bentonite grounding composite materials, and calcium-based bentonite grounding composite materials of the leading indicators of the performance of the test, and its simulation of the buried piece of the experiments and water retention Experiments, the results show that:
In the calcium-based bentonite doped with different mass fractions of Zn, Fe, Al, graphite, carbon black, and carbon fiber, the results show that with the increase in the mass fraction of conductive particles, the resistivity gradually decreases and then tends to a stable value; conductive particles of the density, particle size, dispersion and axial diameter ratio of the resistivity of the composite material has a significant influence;
In calcium-based bentonite, sodium nitrite, sodium molybdate, sodium silicate, sodium chromate, sodium borate, sodium polyphosphate and sodium phosphate on Q235 (yield point (σs) for 235MPa carbon structural steel) have good corrosion resistance; comprehensive consideration of corrosion resistance and environmental protection and economic effects and other factors, and finally determine the sodium molybdate, sodium polyphosphate as a suitable corrosion inhibitor for calcium-based bentonite; through orthogonal experiments Research, to determine the calcium-based bentonite grounding composite materials of various mass fractions of the optimal process program: carbon fiber 2.5%, graphite 9%, sodium polyphosphate 1.5%, sodium molybdate 1.5%, 40% conductive cement, calcium-based bentonite 45.5%; on the corrosion rate of Q235 is low, the size of 0.027mm / a, the corrosion products are FeO (OH), Fe2 (CO3) ( OH), Ca2.8, Fe8.7Al1.2Si0.8 (OH), Fe2O3, Fe3O4; water retention experiments show that: the water content of the composite material of the water retention of the impact is small, while the temperature on the water retention of the effects of water retention is greater when the temperature of 30 ℃ composite material of the water retention of the best; the leading indicators of the test indexes to meet the electric power industry requirements for the lowering of resistance agent.
2.3 Magnesium-based bentonite
Hu Yang [8] in the bentonite modification and its effect on the permeability of cementitious materials in the article the study of different types of bentonite raw materials, heating temperature, different modifier types, and concentration of bentonite magnesium modification of the impact. The results show that with the use of calcium-based bentonite modification, the higher the temperature, the greater the degree of calcium-based bentonite magnesium; the use of sodium-based bentonite modified by the test at room temperature conditions can be realized to the magnesium-based bentonite conversion.
In general, the molar concentration of Mg2 + in the modifier in 0.5 mol / L can meet the needs of the bentonite magnesium, which, using magnesium sulfate as a modifier, can generate magnesium-based bentonite to a greater extent. Before and after the modification of the bentonite was analyzed, calcium-based bentonite and modified magnesium-based bentonite interlayer ionic gravitational effects are significant, able to adsorb more water molecules, the microscopic laminar structure is denser and weaker water-absorbing capacity. In contrast, the sodium-based bentonite interlayer ionic charge gravitational effect is small, the adsorption of water molecules is small, the microscopic laminar structure is more sparse, and the water-absorbing capacity is strong.
In addition, the article also studied the calcium-based bentonite, sodium-based bentonite, and modified magnesium-based bentonite on the mortar work performance, strength properties, anti-permeability properties, and combined with SEM/EDS, MIP test analysis to explore the role of the modified before and after the bentonite to improve the waterproofing and anti-permeability performance of mortar mechanism.
Magnesium sulfate and magnesium nitrate were dissolved in ultrapure water to formulate different concentrations of modifier solution. Then Ca-based bentonite, Na-based bentonite, and the configured modifier solution were mixed at a ratio of 1:20 and then placed in a magnetic stirrer, stirring at 1000r/min stirring speed under different stirring temperatures set to stir for six h. Finally, the heating and stirring completed bentonite slurry filtration and dried at 105 ℃; crushing and grinding can obtain modified Mg-bentonite.
2.4 Aluminum (hydrogen)-based bentonite
Sheng Kai [9] in the microwave method for the preparation of aluminum-based column supported bentonite and adsorption performance research, with a place in Liaoning calcium-based bentonite as raw material, its sodic modification as a carrier, the use of microwave method for the preparation of aluminum-based column supported bentonite, iron aluminum column supported bentonite, zirconium aluminum column supported bentonite, and then a variety of test means of the column after the bentonite characterization, and to explore the adsorption of its simulation of dyes in the wastewater of the optimal conditions.
03、Application areas of bentonite
3.1 Treatment of aquaculture wastewater
Shao Hong et al. used aluminum chloride hexahydrate and sodium dodecyl sulfate composite-modified bentonite. They prepared a modified bentonite with high adsorption performance with a dosage of 3g, stirring time of 20min, stirring speed of 200r/min, ammonia nitrogen wastewater concentration of 300mg/L, and ammonia nitrogen removal rate of 88.41%. Meng Hailing used high-efficiency microwave radiation method, respectively, iron sulfate and aluminum sulfate as a modifier; the preparation of iron sulfate modified sodium bentonite and aluminum sulfate modified sodium bentonite, the two modified soil pore space, layer spacing, and specific surface area are significantly increased, adsorption performance is improved dramatically, the two modified bentonite phosphorus removal rate in water are more than 98%.
3.2 Bentonite waterproofing blanket
A bentonite waterproofing blanket is bentonite particles by specific quality requirements uniformly laid between the two geotextiles; through needle punching and other processes made of a composite waterproofing material containing small gaps, civil engineering fabrics mainly play a protective role. Bentonite waterproofing blankets primarily use the bentonite expansion principle, waterproofing blanket used within the nano-bentonite can be expanded at least dozens of times in contact with water, relying on the needle-punched fibers to the bentonite locked between the two layers of geotextile, forming a viscous high and hydraulic permeability coefficient is tiny uniform, dense colloidal system, can be effective waterproofing.
Bentonite waterproofing blankets in the late 1980s for the first time in landfills, underground garages, artificial lakes, and many other industrial and civil engineering seepage controls. The practice has proved that bentonite waterproofing blankets have been more widely used. Now, bentonite waterproofing blankets as the project seepage control materials have been recognized worldwide.
There are currently three main types of bentonite waterproofing blankets. The raw materials are sodium-based or calcium-based bentonite, but the production method is not the same.
Bentonite waterproofing blankets are used in various fields of waterproof seepage control. Mainly to solve the waterproof seepage problems of multiple projects. In landfill use, the use of bentonite waterproofing blanket seepage control and reinforcement; used in water conservancy projects, bentonite waterproofing blanket can not only improve the seepage control of the irrigation canal but also strengthen the strength of the dam and embankment to reduce soil erosion, to solve the barrier of the hidden danger of the pipe surge; subway project applications, the primary use of bentonite waterproofing blanket waterproofing and seepage control, to prevent the underground buildings are water infiltration, resulting in economic losses, to improve the service life of underground engineering; used in metal tailings ponds, mainly to prevent metal ions stored for a long time, infiltration of the surrounding rocks and water, resulting in unnecessary environmental pollution and endangerment of human health and other issues; in the mines, artificial lakes, tunnels, swimming pools, etc., can improve the waterproofing reliability and durability.
3.3 Bentonite-cement slurry impermeable wall
The bentonite-cement slurry impermeable wall, that is, with ordinary silicate cement, bentonite, and water according to a certain proportion of the configuration of the slurry liquid into the pre-punched groove and the formation of an impenetrable wall with good anti-infiltration properties. From the 1950s, European countries used cement-bentonite vertical impermeable wall technology to prevent the spread of contaminated groundwater, and then the technology extended to reservoirs and dams, lakes, and even heavy metal waste or high-level waste landfill disposal; however, the chemical composition of the groundwater environment and pollutants will be with the cement – bentonite solids to produce a mutual reaction, which will hurt the wall. However, chemicals and contaminants in the groundwater environment can interact with cement-bentonite solids, which can significantly impact the wall’s permeability and strength properties.
In addition, bentonite can be manufactured into bentonite mastics, and bentonite stops for waterproofing of construction or prefabricated joints.
Bentonite is a clay mineral with abundant reserves in China. The main component is montmorillonita. With good physical and chemical properties, it is known as “universal clay.” It can be used as a binder, suspending agent, thixotropic agent, stabilizer, purification, decolorant, filling material, feed, catalyst, etc., and is widely used in metallurgy, petroleum, foundry, food, chemical industry, environmental protection, and other industrial sectors. With the expansion of today’s applications, bentonite research is also constantly updated.